Generating documentation with dbt Docs
dbt natively supports a comprehensive documentation website full of possibilities.
Part of the “Mastering dbt” series. Access to the full Study Guide. Let’s connect on LinkedIn!
Notes from the Documentation and dbt docs documentation.
It’s important to keep a thorough, up-to-date documentation of your projects so users and colleagues can quickly understand the content of the datasets.
dbt enables developers to easily configure and generate documentation for their projects using descriptions and commands.
The documentation generated includes an overview of the project structure, descriptions of tables and columns, and information about the data warehouse.
dbt Docs is the feature available in the free plans, while paid users can use dbt Catalog. We’ll focus on dbt Docs here.
Adding descriptions to your project
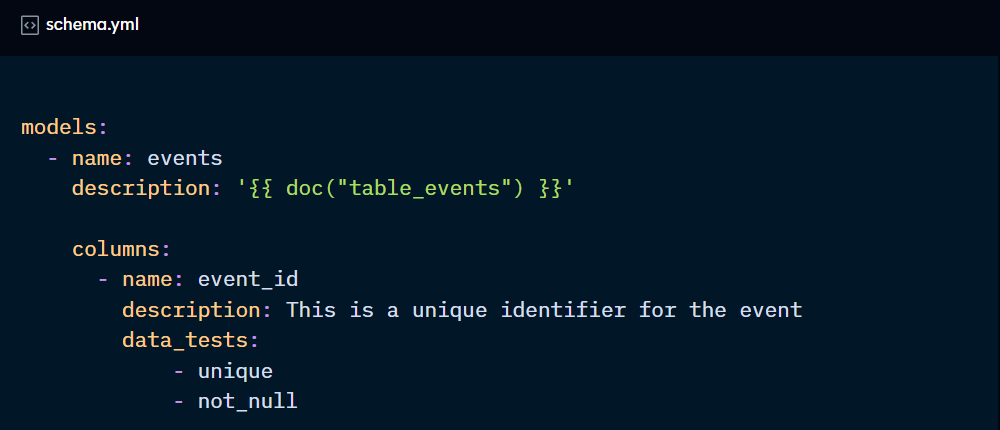
Start by adding descriptions to tables and columns. They should be added to the same file where the data tests are declared.
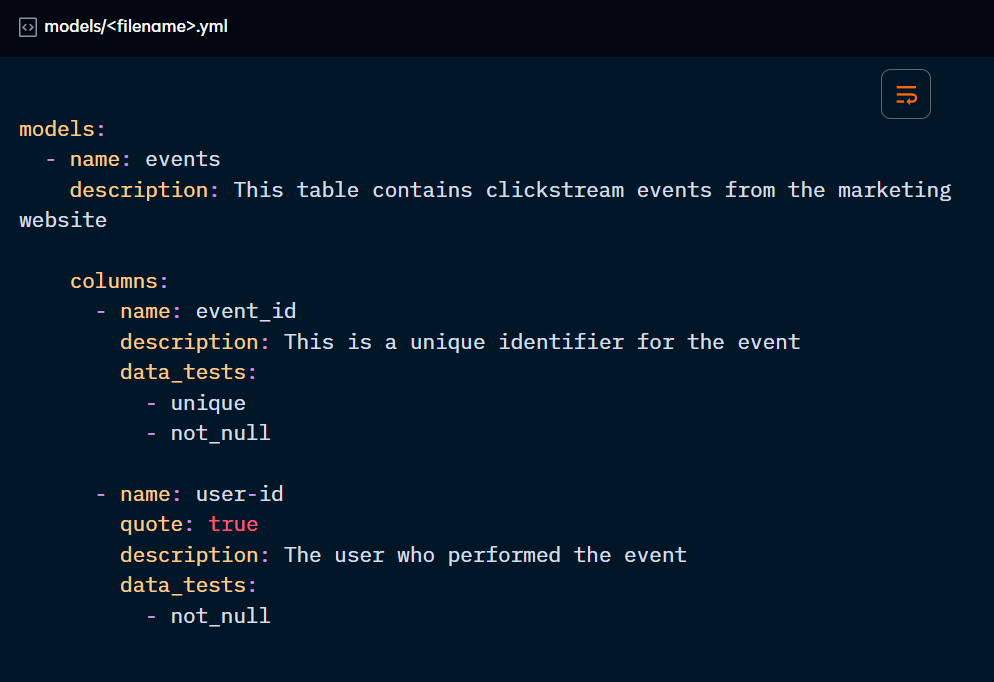
If you need a description longer than one sentence, use “>”:
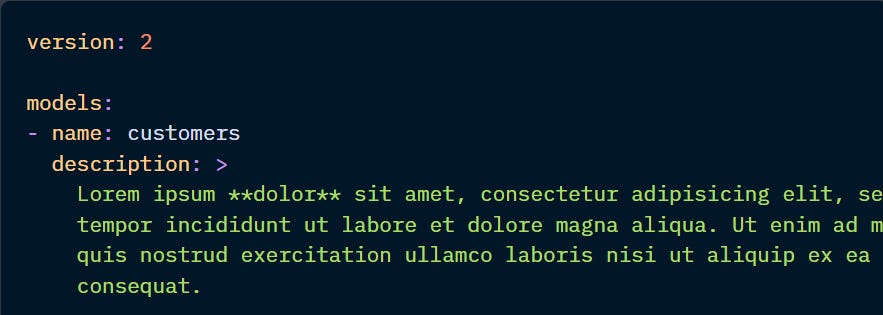
And to insert line breaks, use “|”:
You can also use a docs block to add more robust descriptions to your files.
Using docs blocks
Docs blocks allow developers to use Jinja and markdown in the descriptions.
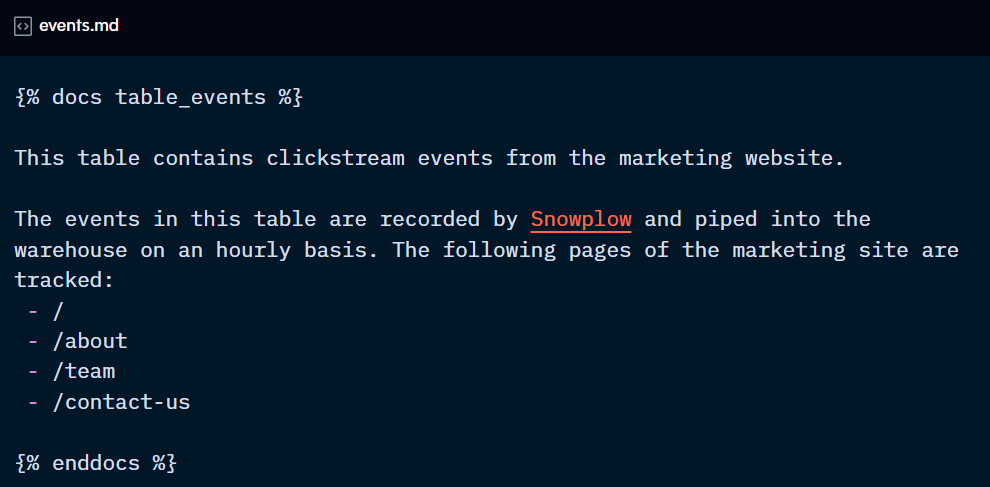
You then point a description config to the relevant docs block using the doc( ) function:
Docs block files need to be uniquely named and use the “docs” Jinja tag. Their name can contain alphanumeric digits and underscores, but it cannot start with a number. The file type is .md.
dbt will look for docs blocks in all resource paths. Alternatively, you can place all docs blocks in one folder and point “docs-path” to it.
Using docs blocks for the overview page
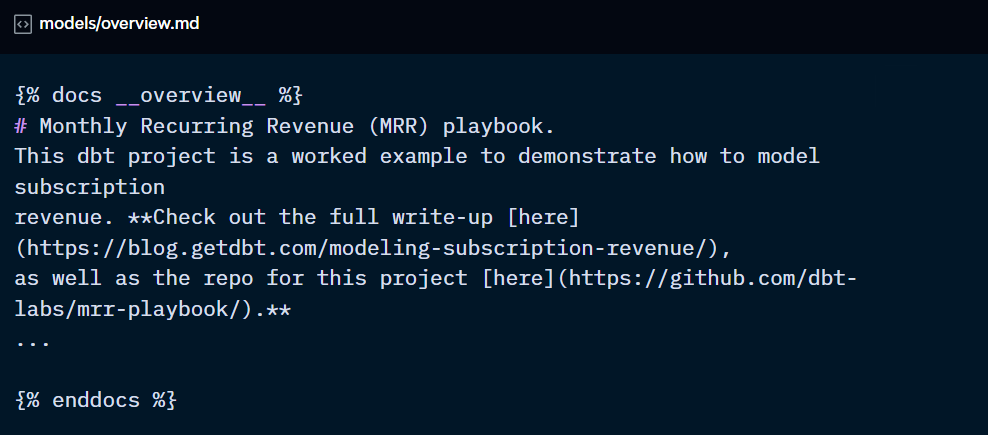
Within your docs website, dbt creates a default overview page with helpful information about the project.
You can override this with specific information about your company's style guide, links to reports, or relevant contact information.
Using the dbt docs commands
dbt docs has two supported commands: generate and serve. They can be run in the command line or, if using the IDE, set to be run during a job.
dbt docs generate
This command generates the documentation website following these steps:
Copying an “index.html” into the “target/” directory.
Compiling the code and adding it to manifest.json.
Stores data warehouse metadata in the catalog.json file.
The combination of manifest.json and catalog.json makes up the data that powers the docs website.
Methods available for dbt docs generate:
You can use the “--select” method to only add specific nodes to catalog.json:

The “--no-compile” method skips step 2, that is, it skips compilation.

The “--empty-catalog” does not populate the catalog.json, which can speed up the command in development. However, in production, you can end up excluding valuable warehouse information from the docs, like column types, stats, sample values, etc.

Use the “--static” method to generate a static page for hosting in cloud providers. When you generate a docs site, you still need to serve it (more on that below), so the index.html, manifest.json, and catalog.json files get loaded into the front end.
With this method, dbt creates a standalone index.html file that can be used externally.

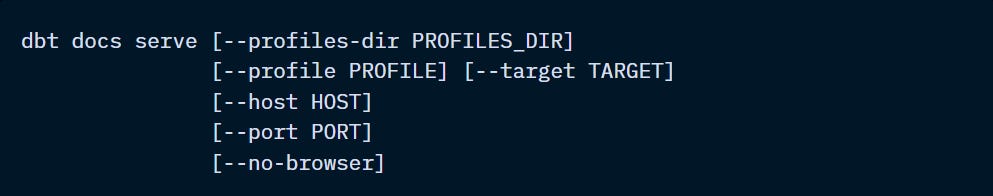
dbt docs serve
After generating documentation with “dbt docs generate”, this command starts a web server on port 8080 to serve your documentation locally and launches it using the default browser.
You can also use several flags to adjust how this server is created: